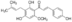
Caftaric acid
Caftaric acid Specification
- Molecular Weight
- 312.23 Grams (g)
- Molecular Formula
- C13H12O9
- Melting Point
- 146-147°
- Usage
- Description: Caftaric acid is a non-flavanoid that impacts the color of white wine. Many believe this molecule is responsible for the yellowish-gold color seen in some whites wines[citation needed]. Aside from wine, it is abundantly present in raisins.
- Purity
- ≥97.0%
Caftaric acid Trade Information
- Minimum Order Quantity
- 1 Kilograms
- Payment Terms
- Cash in Advance (CID), Cash Advance (CA)
- Supply Ability
- 500 Kilograms, , Per Month
- Delivery Time
- 3-4 Week
- Sample Available
- Yes
- Sample Policy
- Sample costs shipping and taxes has to be paid by the buyer
- Main Export Market(s)
- Western Europe, Australia, Middle East, Central America, Eastern Europe, Africa, South America, Asia, North America
- Main Domestic Market
- All India
About Caftaric acid
Caftaric acid analytical standard Synonym: 2-Caffeoyl-L-tartaric acid CAS Number 67879-58-7 Empirical Formula (Hill Notation) C13H12O9 Molecular Weight 312.23 grade analytical standard assay 98.0% (HPLC) form neat shelf life limited shelf life, expiry date on the label application(s) HPLC: suitable gas chromatography (GC): suitable impurities 5.0% waterFAQs of Caftaric acid:
Q: What is the molecular formula of Caftaric acid?
A: The molecular formula of Caftaric acid is C13H12O9.Q: What is the melting point of Caftaric acid?
A: The melting point of Caftaric acid is 146-147C.Q: What is the purity level of Caftaric acid?
A: The purity level of Caftaric acid is 97.0%.Q: What is the molecular weight of Caftaric acid?
A: The molecular weight of Caftaric acid is 312.23 grams (g).Q: What is the primary use of Caftaric acid?
A: Caftaric acid is a non-flavonoid molecule that impacts the color of white wine, contributing to a yellowish-gold hue observed in some white wines. It is also abundantly present in raisins.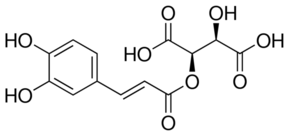

Price:
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
More Products in Analytical Grade Chemicals Category
Carbidopa impurity mixture
Melting Point : Varies based on components in the mixture
Molecular Formula : Varies based on specific impurities (e.g. C10H14N2O4 for Carbidopa)
Molecular Weight : Varies based on specific impurities
Usage : Used to identify and quantify impurities in Carbidopa formulations
Bromate Standard for IC
Price 100 INR
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Kilograms
Melting Point : 350 C (662 F; 623 K)
Molecular Formula : BrO3
Molecular Weight : 167 Grams (g)
Usage : Potassium bromate is typically used in the United States as a flour improver (E number E924). It acts to strengthen the dough and to allow higher rising. It is an oxidizing agent, and under the right conditions will be completely reacted to a form with a lower oxidation state in baking the bread.
Bupivacaine hydrochloride
Price 100 INR
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Kilograms
Melting Point : 258.5°C
Molecular Formula : C18H29ClN2O
Molecular Weight : 324.89 Grams (g)
Xanthohumol
Price 100 INR
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 , , Kilograms
Melting Point : 157–159 °C (315–318 °F; 430–432 K)
Molecular Formula : C21H22O5
Molecular Weight : 354.39 Grams (g)
Usage : Traditional medicinal indications included the treatment of anxiety and insomnia, mild pain reduction or combating dyspepsia (Zanoli and Zavatti, 2008). Today, hops are used in the manufacturing of beer and female infertile plants are cultivated on high trolleys especially for brewing (Figure 1A).

 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry


 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry Send SMS
Send SMS