HEPES
HEPES Specification
- Appearance
- white crystalline powder
- Usage
- HEPES is widely used in cell culture, largely because it is better at maintaining physiological pH despite changes in carbon dioxide concentration (produced by aerobic respiration) when compared to bicarbonate buffers, which are also commonly used in cell culture.
- Molecular Formula
- C8H18N2O4S
- Molecular Weight
- 238.3012 Grams (g)
- Melting Point
- 234 °C
HEPES Trade Information
- Minimum Order Quantity
- 1 Kilograms
- Payment Terms
- Cash in Advance (CID), Cash Advance (CA)
- Supply Ability
- 500 Kilograms KG Per Month
- Delivery Time
- 2-8 Week
- Sample Available
- Yes
- Sample Policy
- Sample costs shipping and taxes has to be paid by the buyer
- Packaging Details
- Carton and Poly Bag.
- Main Export Market(s)
- South America, Western Europe, Australia, North America, Eastern Europe, Middle East, Africa, Central America, Asia
- Main Domestic Market
- All India
About HEPES
HEPESPharmaceutical Secondary Standard;Synonym: 4-(2-Hydroxyethyl)piperazine-1-ethanesulfonic acid, HEPES, N-(2-Hydroxyethyl)piperazine-N-(2-ethanesulfonic acid)CAS Number7365-45-9Empirical Formula (Hill Notation)C8H18N2O4SMolecular Weight238.30PropertiesRelated CategoriesAdditional Standards,Analytical Standards,Analytical/Chromatography,Chromatography,Pharmaceutical Secondary Standards,Pharmaceutical and Drug Standards,Pharmacopeia & Metrological Institutes Standards,Secondary Pharmaceutical Standardspharmaceutical secondary standardInChI Key JKMHFZQWWAIEOD-UHFFFAOYSA-NpH 5.0-6.5 (25C, 238g/L)useful pH range 6.8 - 8.2pKa (25C) 7.5FAQs of HEPES:
Q: What is the primary usage of HEPES in cell culture?
A: HEPES is widely used in cell culture because it is better at maintaining physiological pH despite changes in carbon dioxide concentration during aerobic respiration, compared to bicarbonate buffers.Q: What is the molecular weight of HEPES?
A: The molecular weight of HEPES is 238.3012 grams (g).Q: What is the appearance of HEPES?
A: HEPES appears as a white crystalline powder.Q: What is the melting point of HEPES?
A: The melting point of HEPES is 234 C.Q: What is the molecular formula of HEPES?
A: The molecular formula of HEPES is C8H18N2O4S.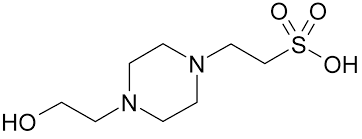

Price:
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
More Products in Analytical Grade Chemicals Category
Ground water (trace elements, high level)
Melting Point : 0C (32F) for water; can vary slightly with impurities
Molecular Formula : H2O (with trace elements such as Fe Mn Zn etc.)
Molecular Weight : 18.015 g/mol (for water itself excludes trace elements)
Usage : Can be consumed after proper treatment; used for irrigation and as a baseline in environmental studies for trace element analysis
Gasoline in Water - PT
Melting Point : N/A (mixture of hydrocarbons)
Molecular Formula : CnH2n+2 (varies based on composition)
Molecular Weight : Varies (~100110 g/mol depending on hydrocarbons)
Usage : Primarily used as a reference material for water contamination monitoring and analysis
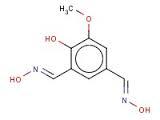
Crocetin dialdehyde
Price 100 INR
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Kilograms
Melting Point : 285 °C (545 °F; 558 K)
Molecular Formula : C20H24O2
Molecular Weight : 296.4 Grams (g)
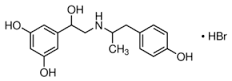
Fenoterol hydrobromide
Price 100 INR
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Kilograms
Melting Point : 222225°C
Molecular Formula : C17H22BrNO4
Molecular Weight : 384.3 Grams (g)
Usage : Fenoterol hydrobromide is the hydrobromide salt of fenoterol. A beta2adrenergic agonist, it is used as a bronchodilator in the management of reversible airway obstruction. It has a role as a bronchodilator agent, a betaadrenergic agonist and a sympathomimetic agent.

 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry



 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry Send SMS
Send SMS Call Me Free
Call Me Free