1,2-Diphenylhydrazine
1,2-Diphenylhydrazine Specification
- Usage
- It does not evaporate easily but may be released to air when attached to dust particles. 1,2-Diphenylhydrazine is a man-made chemical that was used in the past to make benzidine which was used to make various fabric dyes. Benzidine dyes are no longer used in the United States, but may still be used in other countries.
- Melting Point
- 19.5 °C
- Molecular Formula
- C6H8N2
- Purity
- 98%
- Molecular Weight
- 108.14 Grams (g)
1,2-Diphenylhydrazine Trade Information
- Minimum Order Quantity
- 1 Kilograms
- Payment Terms
- Cash in Advance (CID), Cash Advance (CA)
- Supply Ability
- 500 Kilograms, , Per Month
- Delivery Time
- 2-8 Week
- Sample Available
- Yes
- Sample Policy
- Sample costs shipping and taxes has to be paid by the buyer
- Packaging Details
- Carton and Poly Bag.
- Main Export Market(s)
- Western Europe, Middle East, Central America, Eastern Europe, Africa, South America, Australia, North America
- Main Domestic Market
- All India
About 1,2-Diphenylhydrazine
1,2-Diphenylhydrazine Analytical standard, ampule of 100mg Synonym: N,N-Diphenylhydrazine, N,N-Bianiline, Hydrazobenzene, NSC 3510 CAS Number 122-66-7 Linear Formula C6H5NHNHC6H5 Molecular Weight 184.24 grade analytical standard form neat packaging ampule of 100mg application(s) HPLC: suitable gas chromatography (GC): suitable mp 123-126 C(lit.) format neat Application Reactant involved in: Insertion reactions with organometallic tantalum complexes[]Reduction reactions catalyzed by titanium(III) trichloride yielding amines[]Studying the mechanism of hydrazobenzene rearrangement[]Reaction with N-heterocyclic stable silylene[]Synthesis of dimanganese amide hydrazide cluster complexes[]Iron-mediated hydrazine reductions yielding iron arylimide cubanes[]FAQs of 1,2-Diphenylhydrazine:
Q: What is the melting point of 1,2-Diphenylhydrazine?
A: The melting point of 1,2-Diphenylhydrazine is 19.5 C.Q: What is the purity level of 1,2-Diphenylhydrazine?
A: The purity level of 1,2-Diphenylhydrazine is 98%.Q: What is the molecular formula of 1,2-Diphenylhydrazine?
A: The molecular formula of 1,2-Diphenylhydrazine is C6H8N2.Q: What is the molecular weight of 1,2-Diphenylhydrazine?
A: The molecular weight of 1,2-Diphenylhydrazine is 108.14 Grams (g).Q: How does 1,2-Diphenylhydrazine release into the air?
A: 1,2-Diphenylhydrazine does not evaporate easily but may be released to air when attached to dust particles.Q: What was the past usage of 1,2-Diphenylhydrazine?
A: 1,2-Diphenylhydrazine was used in the past to make benzidine, which was utilized to produce various fabric dyes.Q: Are benzidine dyes still in use today?
A: Benzidine dyes are no longer used in the United States, but may still be used in other countries.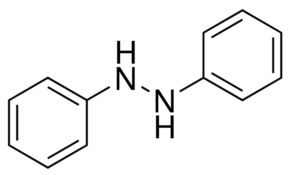

Price:
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
More Products in Analytical Grade Chemicals Category
Alkylphenol Target Analyte Mix solution
Molecular Weight : Varies depending on the specific analytes
Molecular Formula : Varies by individual alkylphenols
Purity : Highpurity standards in trace concentrations
Usage : Used as a standard solution for identifying and quantifying alkylphenol compounds in analytical applications
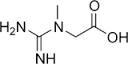
Creatine
Price 100 INR
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 , , Kilograms
Molecular Weight : 131.13 Grams (g)
Molecular Formula : C4H11N3O3
Usage : It helps your muscles produce energy during heavy lifting or highintensity exercise. Taking creatine as a supplement is very popular among athletes and bodybuilders in order to gain muscle,
Isodrine
Price 100 INR
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Kilograms
Molecular Weight : 165.23 Grams (g)
Molecular Formula : C10H15NO
Purity : 99%
trans-Permethrin solution
Price 100 INR
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Kilograms
Molecular Weight : 391.28 Grams (g)
Molecular Formula : C21H20Cl2O3
Purity : 97%
Usage : As a medication, it is used to treat scabies and lice. It is applied to the skin as a cream or lotion. As an insecticide, it can be sprayed on clothing or mosquito nets to kill the insects that touch them. Side effects include rash and irritation at the area of use.

 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry



 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry Send SMS
Send SMS Call Me Free
Call Me Free