Anions in Soil
Anions in Soil Specification
- CAS No
- Varies based on the anion type (e.g. NO3-: 14797-55-8 SO4-2: 14808-79-8)
- Density
- Gram per cubic centimeter(g/cm3)
- Solubility
- Highly soluble in water
- EINECS No
- Varies by anion type
- Molecular Formula
- Varies by anion type (e.g. NO3- SO4- Cl-)
- Usage
- Used to identify nutrient availability and soil health for crops
- Structural Formula
- Depends on the anion type (e.g. NO3- for nitrate SO4-2 for sulfate)
- Ingredients
- Anions such as nitrate (NO3-) sulfate (SO4-2) chloride (Cl-) in soil samples
- Application
- Environmental monitoring soil fertility assessment agricultural management
- Storage
- Store soil samples in a cool dry place and test solutions in sealed containers
- Shape
- N/A in solution form; associated with molecular geometry of the anions
- Purity
- Depends on the composition of soil extract and test preparation
- Properties
- Ionic compounds high solubility in water essential for plant nutrition
- Physical Form
- Other
- Smell
- Odorless
- Grade
- Analytical grade (tests for determining soil composition)
- Poisonous
- NO
- HS Code
- 3822.00
- Appearance
- Typically analyzed as a clear or slightly cloudy solution when extracted
- Taste
- Neutral
- Ph Level
- Depends on concentration and anion type; generally pH neutral to slightly acidic or alkaline
About Anions in Soil
FAQs of Anions in Soil:
Q: What are Anions in Soil primarily used for?
A: They are used to determine soil fertility, nutrient availability, and soil health essential for agricultural and environmental management.Q: Are Anions in Soil safe to use?
A: Yes, they are non-poisonous, odorless, and safe to handle when used as directed.Q: What storage conditions are required?
A: Store soil samples in cool, dry places and test solutions in sealed containers to maintain their integrity.Q: What makes these anions essential for plant nutrition?
A: They are highly soluble in water and provide key nutrients like nitrate, sulfate, and chloride vital for plant growth.Q: Does the pH level affect their properties?
A: Yes, the pH level depends on the concentration and type of anion, ranging from neutral to slightly acidic or alkaline.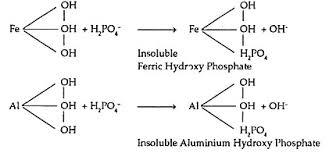

Price:
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
More Products in Analytical Grade Chemicals Category
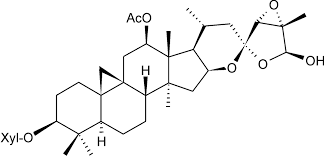
Actaea racemosa for assay CRS
Molecular Formula : C27H40O12
Melting Point : 230235C
Molecular Weight : 540.61 g/mol
Appearance : Offwhite to light yellow powder
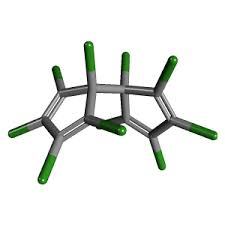
Dienochlor
Price 100 INR
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Kilograms
Molecular Formula : C10Cl10
Melting Point : 122–123 °C (252–253 °F; 395–396 K)
Molecular Weight : 474.6 Grams (g)
Appearance : Yellow crystalline solid
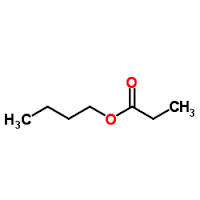
Butyl propionate
Price 100 INR / Kilograms
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Kilograms
Molecular Formula : C7H14O2
Melting Point : 90C
Molecular Weight : 130.2 Grams (g)
Appearance : Clear colorless
Haloperidol for system suitability
Price 100 INR
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Kilograms
Molecular Formula : C21H23ClFNO2
Melting Point : 151.5 ºC
Molecular Weight : 375.9 Grams (g)
Appearance : White to faintly yellow powder

 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry


 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry Send SMS
Send SMS Call Me Free
Call Me Free