Coal (F)
Coal (F) Specification
- Refractive Rate
- Not applicable in solid form
- Melting Point
- Does not have a fixed melting point; decomposes at high temperature
- Density
- 1.5 Gram per cubic centimeter(g/cm3)
- Physical Form
- Solid
- Storage
- Store in a cool dry and well-ventilated area away from ignition sources
- Usage
- Used in power plants steel manufacturing and as a raw material in the production of chemicals
- Appearance
- Black or dark brown often shiny or matte
- Molecular Weight
- Varies depending on grade; primarily around 12 g/mol for pure carbon
- Application
- Fuel source electricity generation steel production chemical feedstock
- HS Code
- 2701.12 (Bituminous coal) or 2702.00 (Lignite and other lower-grade coals)
- Ingredients
- Primarily carbon hydrogen oxygen sulfur nitrogen and trace impurities
- Purity
- Varies widely; ranges from 50-98% carbon depending on type
- Shelf Life
- Indefinite when stored properly
- EINECS No
- Not individually listed; varies by specific coal type and grade
- Molecular Formula
- C
- Structural Formula
- C (amorphous carbon with varying impurities)
- Ph Level
- Neutral to slightly acidic (6-7) depending on composition
- Smell
- Odorless or faint smoky aroma
- Grade
- Industrial-grade fuel-grade or metallurgical-grade options
- Solubility
- Insoluble in water and most organic solvents
- CAS No
- Not specific general CAS: 129521-66-7 (specific forms of coal may differ)
- Poisonous
- NO
- Shape
- Irregular lumps or crushed to granular or powdered form
- Properties
- Amorphous solid combustible variable hardness and density impure carbon with trace elements and minerals
- Taste
- Tasteless
About Coal (F)
Coal (F) is a versatile solid fuel source primarily composed of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and sulfur along with trace impurities. It appears in irregular lumps, granular, or powdered form, ranging from shiny black to matte dark brown. Known for its ability to combust at high temperatures, Coal (F) serves critical industries such as electricity generation, steel production, and chemical manufacturing. With a density of 1.5 g/cm, its purity often ranges from 50-98% carbon, depending on grade. It releases faint smoky aromas but remains tasteless and non-poisonous, making it safe for industrial applications. Coal (F) must be stored in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area away from ignition sources to ensure indefinite shelf life. Insoluble in water and organic solvents, it maintains neutral to slightly acidic pH levels. Its industrial/metallurgical-grade classification supports applications such as power plants and steel manufacturing processes.
FAQs of Coal (F):
Q: What is the primary composition of Coal (F)?
A: Coal (F) primarily consists of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, and trace impurities.Q: What are the typical applications of Coal (F)?
A: Coal (F) is used for electricity generation, steel production, and as a chemical feedstock.Q: Is Coal (F) poisonous?
A: No, Coal (F) is non-poisonous.Q: Can Coal (F) dissolve in water?
A: No, Coal (F) is insoluble in water and most organic solvents.Q: How should Coal (F) be stored?
A: Store Coal (F) in a cool, dry, and ventilated area away from ignition sources.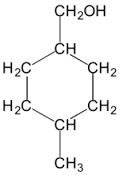
Tell us about your requirement

Price:
Quantity
Select Unit
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
Additional detail
Mobile number
Email
More Products in Analytical Grade Chemicals Category
-Alumina (1.05 m2/g) (nitrogen BET specific surface area)
Molecular Formula : Al2O3
Purity : 99.5%
Molecular Weight : 101.96 g/mol
Appearance : White powder
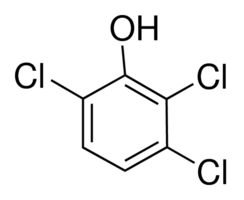
2, 3,6-Trichlorophenol
Price 100 INR / Kilograms
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Kilograms
Molecular Formula : C6H2Cl3OH
Purity : 97%
Appearance : yellowwhitish lumps or powder
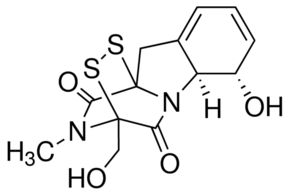
Gliotoxin solution
Price 100 INR
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Kilograms
Molecular Formula : C13H14N2O4S2
Purity : 97%
Molecular Weight : 326.39 Grams (g)
Appearance : White to yellow crystalline solid
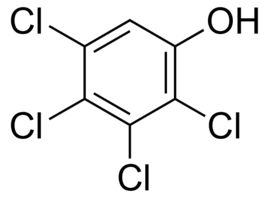
2,3,4,5-Tetrachlorophenol solution
Price 100 INR
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Kilograms
Molecular Formula : C6H2Cl4O
Purity : 98%
Molecular Weight : 231.9 Grams (g)

 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry


 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry Send SMS
Send SMS Call Me Free
Call Me Free