Erbium Standard for AAS
Erbium Standard for AAS Specification
- Molecular Weight
- 167.26 Grams (g)
- Melting Point
- 1,529 °C
- Usage
- Erbium isotopes are good neutron absorbers and are used in nuclear reactor control rods. The oxide erbia is used as a pink coloring agent in glazes and glasses. Erbium is used in alloys especially with vanadium to decrease the hardness of metals. It is also used in amplifiers and lasers.
- Appearance
- Silvery white
- Molecular Formula
- Er
Erbium Standard for AAS Trade Information
- Minimum Order Quantity
- 1 Kilograms
- Payment Terms
- Cash in Advance (CID), Cash Advance (CA)
- Supply Ability
- 500 Kilograms KG Per Month
- Delivery Time
- 2-8 Week
- Sample Available
- Yes
- Sample Policy
- Sample costs shipping and taxes has to be paid by the buyer
- Packaging Details
- Carton and Poly Bag.
- Main Export Market(s)
- Eastern Europe, Central America, Africa, Middle East, South America, Western Europe, Asia, North America, Australia
- Main Domestic Market
- All India
About Erbium Standard for AAS
FAQs of Erbium Standard for AAS:
Q: What is the primary application of erbium isotopes?
A: Erbium isotopes are excellent neutron absorbers, commonly used in nuclear reactor control rods.Q: What makes erbia a valuable material?
A: Erbia is used as a pink coloring agent in glazes and glasses, valued for its aesthetic properties.Q: How does erbium impact metal alloys?
A: Erbium alloys with vanadium to decrease the hardness of metals, improving material characteristics.Q: What industrial uses make erbium significant?
A: Erbium is used in amplifiers and lasers due to its unique optical and electronic properties.Q: What is the melting point of erbium?
A: Erbium has a melting point of 1,529 C, ensuring its stability in high-temperature applications.

Price:
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
More Products in Analytical Grade Chemicals Category
Anions on Filter Paper
Price 100 INR
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Kilograms
Molecular Formula : N/A (Composite product)
Usage : Dip strip into sample solution and compare color change to chart
Trometamol
Price 100 INR
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Kilograms
Molecular Formula : C4H11NO3
Melting Point : 175 °C
Molecular Weight : 121.14 Grams (g)
Usage : This medication is an antibiotic used to treat bladder infections (such as acute cystitis or lower urinary tract infections) in women. It works by stopping the growth of bacteria. This antibiotic treats only bacterial infections.
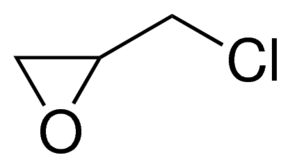
()-Epichlorohydrin
Price 100 INR
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Kilograms
Molecular Formula : C3H5ClO
Melting Point : 25.6 °C
Molecular Weight : 92.52 Grams (g)
Usage : What are the uses for epichlorohydrin? Epichlorhydrin is used for making glycerine and as a monomer/building block for making plastics and other polymers, some of which are used as coagulant aids in water treatment. It is also used in the paper and drug industries as an insect fumigant.
di- Allate
Price 100 INR
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 , , Kilograms
Molecular Formula : C10H17Cl2NOS
Melting Point : 2530 C
Molecular Weight : 270.22 Grams (g)

 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry
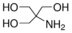


 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry Send SMS
Send SMS Call Me Free
Call Me Free