Ethylenediamine
Ethylenediamine Specification
- Molecular Weight
- 60.1 Grams (g)
- Usage
- Ethylenediamine is used as a very important bidentate ligand forming chelate agents. The main application is to produce chelating agents such as ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA). It is used in the manufacture of carbamate fungicides, surfactant and dyes.
- Melting Point
- 47°F.
- Appearance
- colorless liquid
- Molecular Formula
- C2H8N2
- Density
- 900 Kilogram per cubic meter (kg/m3)
Ethylenediamine Trade Information
- Minimum Order Quantity
- 1 Kilograms
- Payment Terms
- Cash in Advance (CID), Cash Advance (CA)
- Supply Ability
- 500 Kilograms, KG Per Month
- Delivery Time
- 2-8 Week
- Sample Available
- Yes
- Sample Policy
- Sample costs shipping and taxes has to be paid by the buyer
- Packaging Details
- Carton and Poly Bag.
- Main Export Market(s)
- Western Europe, Australia, Eastern Europe, Africa, Middle East, South America, Asia, Central America, North America
- Main Domestic Market
- All India
About Ethylenediamine
Ethylenediamineanalytical standardSynonym: 1,2-DiaminoethaneCAS Number107-15-3Linear FormulaNH2CH2CH2NH2Molecular Weight60.10PropertiesRelated CategoriesAdditional Standards,Aliphatics,Alpha Sort,Amines,Analytical Standards,Analytical/Chromatography,Chemical Class,Chromatography,E,E-L,Environmental Standards,Organic Pollutant Standards,Solvents,Volatile & Semivolatile Standards,Volatiles/ Semivolatilesgrade analytical standardfor GCvapor density 2.07 (vs air)vapor pressure 10 mmHg ( 20 C)InChI Key PIICEJLVQHRZGT-UHFFFAOYSA-Nassay 99.8% (GC)form neatautoignition temp. 716Fshelf life limited shelf life, expiry date on the labelexpl. lim. 16%application(s) HPLC: suitablegas chromatography (GC): suitablerefractive index n20/D1.456n20/D1.4565(lit.)bp 118C(lit.)mp 8.5C(lit.)solubility H2O: soluble atdensity 0.899g/mLat 25C(lit.)format neatFAQs of Ethylenediamine:
Q: What is the molecular formula and molecular weight of Ethylenediamine?
A: The molecular formula of Ethylenediamine is C2H8N2, and its molecular weight is 60.1 grams (g).Q: What is the density of Ethylenediamine?
A: The density of Ethylenediamine is 900 kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m3).Q: What does Ethylenediamine look like?
A: Ethylenediamine is a colorless liquid in appearance.Q: At what temperature does Ethylenediamine melt?
A: Ethylenediamine has a melting point of 47F.Q: What are the main applications of Ethylenediamine?
A: Ethylenediamine is primarily used as a bidentate ligand for forming chelating agents such as ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA). It is also used in the manufacture of carbamate fungicides, surfactants, and dyes.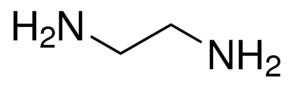

Price:
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
More Products in Analytical Grade Chemicals Category
Carbendazim
Molecular Formula : C9H9N3O2
Appearance : White crystalline powder
Molecular Weight : 191.19 g/mol
Purity : 98%
CEN PCB Congener Mix-1
Molecular Formula : C12HCln
Appearance : Liquid or crystalline solid
Molecular Weight : Varies (depending on congener mix)
Purity : Defined by the manufacturer for calibration purposes; purity generally considered in terms of congener composition
Acetamiprid-N-desmethyl
Price 100 INR
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Kilograms
Molecular Formula : C10H11ClN4
Appearance : white powder
Molecular Weight : 222.678 Grams (g)
Purity : 98%
Dimefluthrin
Price 100 INR
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Kilograms
Molecular Formula : C19H22F4O3
Appearance : Light yellow liquid
Molecular Weight : 374.376
Purity : 95%.

 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry



 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry Send SMS
Send SMS