Glucose monohydrate
MOQ : 1 Kilograms
Glucose monohydrate Specification
- Usage
- Dextrose Monohydrate. Dextrose Monhydrate serves as a sweetener, energy source, bulking agent, and cryoprotectant in an extensive variety of food applications including cakes, pastries, soups, sauces, ice cream, seasonings as well as others. Glucose or dextrose is the monomer of the starch chain (polymers).
- Melting Point
- 146 C
- Purity
- 99%
- Molecular Formula
- C6H14O7
Glucose monohydrate Trade Information
- Minimum Order Quantity
- 1 Kilograms
- Payment Terms
- Cash Advance (CA), Cash in Advance (CID)
- Supply Ability
- 500 Kilograms Per Month
- Delivery Time
- 2-8 Week
- Sample Available
- Yes
- Sample Policy
- Sample costs shipping and taxes has to be paid by the buyer
- Packaging Details
- Carton and Poly Bag.
- Main Export Market(s)
- Australia, North America, Eastern Europe, Middle East, Western Europe, Africa, Central America, South America, Asia
- Main Domestic Market
- All India
About Glucose monohydrate
Glucose monohydrateEuropePharmacopoeia (EP) Reference StandardSynonym: D-(+)-Glucose monohydrate, Dextrose monohydrateCAS Number14431-43-7Empirical Formula (Hill Notation)C6H12O6 H2OMolecular Weight198.17PropertiesRelated CategoriesAnalytical Standards,Analytical/Chromatography,EP Standards,EP Standards G - H,Pharmacopeia & Metrological Institutes StandardsInChI Key SPFMQWBKVUQXJV-BTVCFUMJSA-NFAQs of Glucose monohydrate:
Q: What is the melting point of Glucose Monohydrate?
A: The melting point of Glucose Monohydrate is 146 C.Q: What is the purity level of Glucose Monohydrate?
A: Glucose Monohydrate has a purity level of 99%.Q: What are the common applications of Glucose Monohydrate?
A: Glucose Monohydrate serves as a sweetener, energy source, bulking agent, and cryoprotectant in a variety of food applications, including cakes, pastries, soups, sauces, ice cream, and seasonings, among others.Q: What is the molecular formula of Glucose Monohydrate?
A: The molecular formula of Glucose Monohydrate is C6H14O7.Q: How is Glucose Monohydrate related to starch chains?
A: Glucose or dextrose is the monomer of the starch chain (polymers).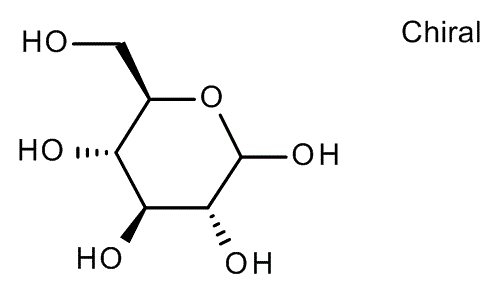
Tell us about your requirement

Price:
Quantity
Select Unit
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
Additional detail
Mobile number
Email
More Products in Analytical Grade Chemicals Category
Immunoglobulin (anti-A, anti-B antibodies test) positive control
Purity : Dependent on supplier; typically meets diagnostic standards
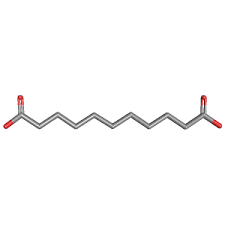
Undecanedioic acid
Price 100 INR
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Kilograms
Molecular Formula : C11H20O4
Purity : 98%
Molecular Weight : 216.2741 Grams (g)
Melting Point : 127–129 °C (261–264 °F; 400–402 K)
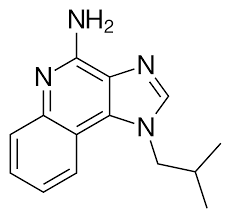
Halofenozide
Price 100 INR
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Kilograms
Molecular Formula : C18H19ClN2O2
Purity : 99%
Molecular Weight : 330.812 Grams (g)
Melting Point : (oC), 200
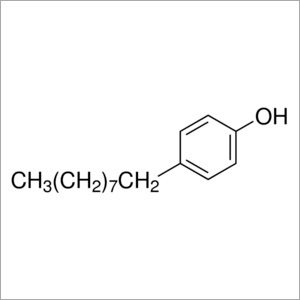
4-Nonylphenol
Price 100 INR
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Kilograms
Molecular Formula : C15H24O
Molecular Weight : 220.35 Grams (g)

 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry


 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry Send SMS
Send SMS