Ground water (trace elements)
Ground water (trace elements) Specification
- Smell
- Odorless or slightly earthy/mineral-like depending on composition
- Ingredients
- Predominantly water (H2O) with trace elements like Fe Mg Ca Na and others
- Shape
- Liquid (no fixed shape)
- Purity
- Varies depending on source and mineral content
- Melting Point
- 0C (pure water; presence of trace elements may shift slightly)
- Solubility
- Water is a universal solvent; trace elements are found dissolved
- Properties
- Varies; includes trace minerals ions and elements depending on source
- Molecular Weight
- 18.015 g/mol (for water; trace elements vary)
- Usage
- Usage varies by industry including drinking water analysis irrigation and research
- Ph Level
- Typically 6.5 to 8.5 (may vary based on trace elements)
- EINECS No
- 231-791-2 (for water; individual elements vary)
- Density
- 1 Gram per cubic centimeter(g/cm3)
- Grade
- Environmental-grade research-grade or industrial-grade
- Physical Form
- Liquid
- Shelf Life
- Indefinite if stored correctly; avoid contamination
- Storage
- Store in clean contamination-free environments at room temperature
- CAS No
- 7732-18-5 (for water; individual trace elements have separate CAS numbers)
- Appearance
- Clear colorless
- Taste
- Neutral varies based on trace elements present
- Refractive Rate
- 1.333 (pure water; may vary with content)
- HS Code
- 2853.00 (for water analysis samples; varies by trace elements)
- Poisonous
- NO
- Application
- Environmental studies health monitoring agricultural analysis industrial processes
- Molecular Formula
- Varies; predominantly H2O with trace amounts of minerals and elements
- Structural Formula
- H2O with dissolved ions and minerals (e.g. Na+ Ca2+ Mg2+)
About Ground water (trace elements)
Ground water (trace elements)PropertiesRelated CategoriesAnalytical Reagents,Analytical Standards,Analytical/Chromatography,Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (AAS),Matrix Standards with Certified Elemental Content,Pharmacopeia & Metrological Institutes Standards,Reference Materials from the European Commissions Joint Research Centre (formerly IRMM),Spectroscopy,Water and Water Pollution Matrix CRMs (Element content)format matrix materialFAQs of Ground water (trace elements):
Q: What are the primary applications of Ground Water (trace elements)?
A: Ground Water (trace elements) is used in environmental studies, health monitoring, agricultural analysis, industrial processes, drinking water analysis, irrigation, and research purposes.Q: How should Ground Water (trace elements) be stored to ensure its shelf life?
A: Store it in clean, contamination-free environments at room temperature to maintain its indefinite shelf life. Avoid contamination to ensure purity.Q: What are the main ingredients in Ground Water (trace elements)?
A: Ground Water (trace elements) primarily consists of water (H2O), with trace elements such as Fe, Mg, Ca, Na, and others dissolved within.Q: Does Ground Water (trace elements) have a specific taste or smell?
A: The taste is neutral but may vary depending on the trace elements present. It is odorless or slightly earthy/mineral-like based on its composition.Q: What is the pH level range of Ground Water (trace elements)?
A: The pH level typically ranges from 6.5 to 8.5, though variations may occur depending on the trace elements present.

Price:
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
More Products in Analytical Grade Chemicals Category
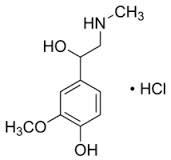
Catecholamine Mix 2 (Metanephrines) solution
Molecular Weight : 183.21 g/mol (for Metanephrines)
Purity : High purity suitable for research and diagnostic use
Molecular Formula : C9H13NO3 (for Metanephrines)
Usage : Used in laboratory research and diagnostic assays to profile catecholamine metabolites
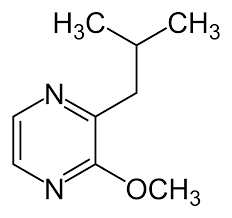
2-Isopropyl-3-methoxypyrazine solution
Price 100 INR / Kilograms
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Kilograms
Molecular Weight : 152.19 Grams (g)
Purity : 95%
Molecular Formula : C8H12N2O
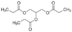
Tripropionin
Price 100 INR
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Kilograms
Molecular Weight : 260.28 Grams (g)
Purity : 95%
Molecular Formula : C12H20O6
Usage : Description: Tripropionin is a triglyceride obtained by formal acylation of the three hydroxy groups of glycerol by propionic acid. It has a role as a flavouring agent. It is a triglyceride and a propanoate ester.
Ginsenoside Rg6
Price 100 INR
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Kilograms
Molecular Weight : 766.5 Grams (g)
Purity : 98%
Molecular Formula : C42H70O12

 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry


 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry Send SMS
Send SMS