Pimelic acid
Pimelic acid Specification
- Purity
- 99%
- Melting Point
- 103 to 105 °C (217 to 221 °F; 376 to 378 K)
- Molecular Formula
- C7H12O4
- Usage
- Pimelic acid is the organic compound with the formula HO2C(CH2)5CO2H. Derivatives of pimelic acid are involved in the biosynthesis of the amino acid called lysine. Pimelic acid is one methylene longer than a related dicarboxylic acid, adipic acid, a precursor to many polyesters and polyamides.
- Molecular Weight
- 160.17 Grams (g)
Pimelic acid Trade Information
- Minimum Order Quantity
- 1 Kilograms
- Payment Terms
- Cash Advance (CA), Cash in Advance (CID)
- Supply Ability
- 500 Kilograms KG Per Month
- Delivery Time
- 2-8 Week
- Sample Available
- Yes
- Sample Policy
- Sample costs shipping and taxes has to be paid by the buyer
- Packaging Details
- Carton and Poly Bag.
- Main Export Market(s)
- Australia, Eastern Europe, Middle East, Central America, Africa, South America, Western Europe, Asia, North America
- Main Domestic Market
- All India
About Pimelic acid
FAQs of Pimelic acid:
Q: What is the purity level of pimelic acid?
A: Pimelic acid has a purity level of 99%.Q: What is the melting point of pimelic acid?
A: The melting point of pimelic acid ranges from 103 to 105 C (217 to 221 F).Q: What is the molecular weight of pimelic acid?
A: Pimelic acid has a molecular weight of 160.17 grams.Q: What are the primary uses of pimelic acid?
A: Pimelic acid is involved in lysine biosynthesis and serves as a precursor in polymer synthesis and organic chemistry applications.Q: How does pimelic acid compare to adipic acid?
A: Pimelic acid is structurally similar to adipic acid but contains one additional methylene group.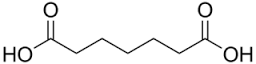

Price:
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
More Products in Analytical Grade Chemicals Category
Gallium atomic absorption standard solution
Price 100 INR
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Kilograms
Molecular Weight : 72.92517 Grams (g)
Molecular Formula : Ga
Appearance : Liquid
Trizma base
Price 100 INR
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Kilograms
Molecular Weight : 121.14 Grams (g)
Molecular Formula : C4H11NO3
Appearance : White crystalline powder
Melting Point : 175 °C
Alternariol-9-methyl ether
Price 100 INR
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Kiloampere
Molecular Weight : 258.226 Grams (g)
Molecular Formula : C14H10O5
Appearance : White to OffWhite powder
Melting Point : 270273ºC (dec.)
Cineole chemical
Price 100 INR
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Kilograms
Molecular Weight : 154.249 Grams (g)
Molecular Formula : C10H18O
Appearance : colorless clear liquid
Melting Point : 1.5 C

 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry


 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry Send SMS
Send SMS