Valeric acid
Valeric acid Specification
- Melting Point
- -34.5 °C
- Density
- 930 Kilogram per cubic meter (kg/m3)
- Molecular Formula
- C5H10O2
- Molecular Weight
- 102.13 Grams (g)
- Usage
- Its primary use is in the synthesis of its esters. Volatile esters of valeric acid tend to have pleasant odors and are used in perfumes and cosmetics. Ethyl valerate and pentyl valerate are used as food additives because of their fruity flavors.
Valeric acid Trade Information
- Minimum Order Quantity
- 1 Kilograms
- Payment Terms
- Cash in Advance (CID), Cash Advance (CA)
- Supply Ability
- 500 Kilograms kg Per Month
- Delivery Time
- 2-8 Week
- Sample Available
- Yes
- Sample Policy
- Sample costs shipping and taxes has to be paid by the buyer
- Packaging Details
- Carton and Poly Bag.
- Main Export Market(s)
- Australia, South America, Eastern Europe, Western Europe, Middle East, Africa, Central America, Asia, North America
- Main Domestic Market
- All India
About Valeric acid
FAQs of Valeric acid:
Q: What are the main uses of valeric acid?
A: Valeric acid is primarily used for the synthesis of esters, which are employed in perfumes, cosmetics, and as food flavoring agents due to their pleasant fruity aromas and flavors.Q: What is the density of valeric acid?
A: The density of valeric acid is 930 kg/m.Q: At what temperature does valeric acid melt?
A: Valeric acid has a melting point of -34.5 C.Q: What makes valeric acid derivatives suitable for food applications?
A: Valeric acid derivatives, such as ethyl valerate and pentyl valerate, have fruity flavors, making them ideal for use as food additives.Q: Which industries primarily use valeric acid?
A: Valeric acid is widely utilized in the fragrance and food industries for esters synthesis used in perfumes, cosmetics, and flavoring applications.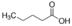

Price:
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
More Products in Analytical Grade Chemicals Category
Gas Chromatography <621> PT
Price 100 INR
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Kilograms
Usage : Sample preparation, separation, testing
D-Gluconic acid sodium salt
Price 100 INR
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Kilograms
Molecular Weight : 196.16 Grams (g)
Melting Point : 131 °C (268 °F; 404 K)
Molecular Formula : C6H12O7
Usage : Gluconate is also an electrolyte present in certain solutions, such as "plasmalyte a", used for intravenous fluid resuscitation. Quinine gluconate is a salt of gluconic acid and quinine, which is used for intramuscular injection in the treatment of malaria. Zinc gluconate injections are used to neuter male dogs.
Haloxyfop-P
Price 100 INR
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Kilograms
Molecular Weight : 361.701 Grams (g)
Melting Point : 5557°C
Molecular Formula : C15H11ClF3NO4
Valine
Price 100 INR
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Kilograms
Molecular Weight : 117.151 Grams (g)
Melting Point : 298 °C
Molecular Formula : C5H11NO2
Usage : Lvaline is used in muscle metabolism and to repair muscle tissue. It is also used to regulate the level of nitrogen in the body.

 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry


 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry Send SMS
Send SMS Call Me Free
Call Me Free