Warfarin
Warfarin Specification
- Molecular Formula
- C19H16O4
- Usage
- Warfarin is an anticoagulant (blood thinner). Warfarin reduces the formation of blood clots. Warfarin is used to treat or prevent blood clots in veins or arteries, which can reduce the risk of stroke, heart attack, or other serious conditions.
- Molecular Weight
- 308.33 Grams (g)
- Melting Point
- 151-161 °C.
- Purity
- 98%
Warfarin Trade Information
- Minimum Order Quantity
- 1 Kilograms
- Payment Terms
- Cash in Advance (CID), Cash Advance (CA)
- Supply Ability
- 500 Kilograms, KG Per Month
- Delivery Time
- 2-8 Week
- Sample Available
- Yes
- Sample Policy
- Sample costs shipping and taxes has to be paid by the buyer
- Packaging Details
- Carton and Poly Bag.
- Main Export Market(s)
- Western Europe, Australia, Eastern Europe, Middle East, Africa, South America, Asia, Central America, North America
- Main Domestic Market
- All India
About Warfarin
FAQs of Warfarin:
Q: What is Warfarin used for?
A: Warfarin is used as an anticoagulant to treat or prevent blood clots in veins or arteries, reducing the risk of stroke, heart attack, or other serious conditions.Q: What is the purity level of Warfarin?
A: Warfarin has a high purity level of 98%.Q: What is the molecular weight of Warfarin?
A: The molecular weight of Warfarin is 308.33 grams (g).Q: What is the molecular formula of Warfarin?
A: The molecular formula of Warfarin is C19H16O4.Q: What is the melting point range of Warfarin?
A: Warfarin has a melting point range of 151-161 C.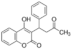

Price:
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
More Products in Analytical Grade Chemicals Category
CFPP Standard
Molecular Weight : 280.45 g/mol
Molecular Formula : C18H32O2
Usage : Primarily used in laboratories for assessing fuel flow characteristics under cold conditions.
Melting Point : 6 C
Potassium dihydrogen phosphate
Price 100 INR
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Kilograms
Molecular Weight : 136.086 Grams (g)
Molecular Formula : KH2PO4
Usage : Monopotassium phosphate, MKP, (also potassium dihydrogenphosphate, KDP, or monobasic potassium phosphate), KH2PO4, is a soluble salt of potassium and the dihydrogen phosphate ion which is used as a fertilizer, a food additive and a fungicide. It is a source of phosphorus and potassium. It is also a buffering agent.
Melting Point : 252.6 °C
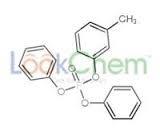
Cresyl diphenyl phosphate
Price 100 INR
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Kilograms
Molecular Weight : 340.3 Grams (g)
Molecular Formula : C19H17O4P
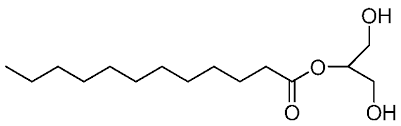
Glycerol monocaprylate
Price 100 INR
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Kilograms
Molecular Weight : 218.29 Grams (g)
Molecular Formula : C11H22O4
Usage : In food and beverages, glycerol serves as a humectant, solvent, and sweetener, and may help preserve foods. It is also used as filler in commercially prepared lowfat foods (e.g., cookies), and as a thickening agent in liqueurs. Glycerol and water are used to preserve certain types of plant leaves.
Melting Point : 34 C

 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry
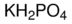


 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry Send SMS
Send SMS