(+)--Pinene
(+)--Pinene Specification
- Molecular Formula
- C10H16
- Appearance
- Liquid
- Density
- 0,86 g·cm−3
- Melting Point
- 211 to 218 K)
- Usage
- pinene is highly repellant to insects and is widely seen terpenoid in the nature. Pinene is found in many essential oils as a main component. It is used in production of many perfumes and deodorants. Alpha pinene is a compound of the oils and resins of numerous plants and is mostly seen in coniferous pine trees.
(+)--Pinene Trade Information
- Minimum Order Quantity
- 1 Kilograms
- Payment Terms
- Cash in Advance (CID), Cash Advance (CA)
- Supply Ability
- 500 Kilograms KG Per Month
- Delivery Time
- 2-8 Week
- Sample Available
- Yes
- Sample Policy
- Sample costs shipping and taxes has to be paid by the buyer
- Packaging Details
- Carton and Poly Bag.
- Main Export Market(s)
- Western Europe, Australia, Central America, Africa, Middle East, South America, Asia, Eastern Europe, North America
- Main Domestic Market
- All India
About (+)--Pinene
(+)--PineneAnalytical standard Synonym: (1R,5R)-2(10)-Pinene, (1R,5R)-6,6-Dimethyl-2-methylenebicyclo[3.1.1]heptane CAS Number 19902-08-0 Empirical Formula (Hill Notation) C10H16 Molecular Weight 136.23 grade analytical standard assay 98.5% (sum of enantiomers, GC) form neat optical activity []20/D +221, neat shelf life limited shelf life, expiry date on the label application(s) HPLC: suitable gas chromatography (GC): suitable refractive index n20/D 1.478(lit.) n20/D 1.478 bp 164-165C(lit.) density 0.872g/mLat 25C(lit.) format neat storage temp. 2-8CFAQs of (+)--Pinene:
Q: What is the molecular formula of (+)--Pinene?
A: The molecular formula of (+)--Pinene is C10H16.Q: What is the physical appearance of (+)--Pinene?
A: (+)--Pinene appears as a liquid.Q: What is the melting point range of (+)--Pinene?
A: The melting point ranges from 211 to 218 K for (+)--Pinene.Q: What is the density of (+)--Pinene?
A: The density of (+)--Pinene is 0.86 gcm.Q: What are the primary usages of (+)--Pinene?
A: (+)--Pinene is highly repellent to insects, widely found in nature as a terpenoid, and a major component of many essential oils. It is used in the production of perfumes and deodorants.Q: In which type of plants is (+)--Pinene commonly found?
A: (+)--Pinene is commonly found in the oils and resins of numerous plants, especially in coniferous pine trees.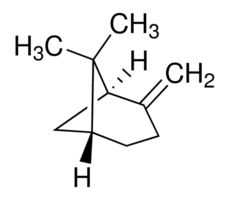

Price:
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
More Products in Analytical Grade Chemicals Category
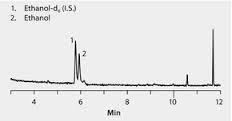
Beer (EtOH, low level)
Molecular Weight : 46.07 g/mol
Molecular Formula : C2H6O
Purity : Low to mild ethanol concentration (2% 12% by volume)
Appearance : Clear golden or amber liquid
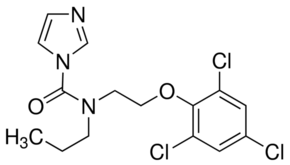
Prochloraz
Price 100 INR
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Kilograms
Molecular Weight : 376.662 Grams (g)
Molecular Formula : C15H16Cl3N3O2
Purity : 99%
Appearance : Of a clear liquid
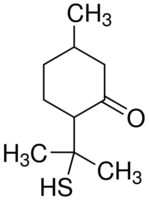
8-Mercaptomenthone
Price 100 INR
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Kilograms
Molecular Weight : 154.253 Grams (g)
Molecular Formula : C10H18O
Appearance : colorless to yellow brown clear liquid
Benzo[b]fluoranthene
Price 100 INR
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Kilograms
Molecular Weight : 252.3093 Grams (g)
Molecular Formula : C20H12
Purity : 99%
Appearance : Offwhite to tan powder

 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry
![Benzo[b]fluoranthene](https://cpimg.tistatic.com/03503481/b/5/Benzo-b-fluoranthene.jpg)


 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry Send SMS
Send SMS