1,4-Benzoquinone
MOQ : 1 Kilograms
1,4-Benzoquinone Specification
- Melting Point
- 115 °C
- Usage
- It is used as a hydrogen acceptor and oxidant in organic synthesis. 1,4-Benzoquinone serves as a dehydrogenation reagent. It is also used as a dienophile in Diels Alder reactions. Benzoquinone reacts with acetic anhydride and sulfuric acid to give the triacetate of hydroxyquinol.
- Appearance
- Yellow solid
- Density
- 1.32 g/cm³
- Purity
- 98%
- Molecular Weight
- 108.095 g/mol Grams (g)
- Molecular Formula
- C6H4O2
1,4-Benzoquinone Trade Information
- Minimum Order Quantity
- 1 Kilograms
- Payment Terms
- Cash Advance (CA), Cash in Advance (CID)
- Supply Ability
- 500 Kilograms, , KG Per Month
- Delivery Time
- 2-8 Week
- Sample Available
- Yes
- Sample Policy
- Sample costs shipping and taxes has to be paid by the buyer
- Packaging Details
- Carton and Poly Bag.
- Main Export Market(s)
- Western Europe, Central America, Eastern Europe, Africa, Middle East, South America, Australia, Asia, North America
- Main Domestic Market
- All India
About 1,4-Benzoquinone
1,4-Benzoquinone Pharmaceutical secondary standard; traceable to USP Synonym: p-Benzoquinone, Quinone CAS Number 106-51-4 Linear Formula C6H4(=O)2 Molecular Weight 108.09 grade certified reference material pharmaceutical secondary standard vapor density 3.73 (vs air) vapor pressure 0.1 mmHg ( 25 C) form neat autoignition temp. 815 F mp 113-115 C(lit.) format neat pharmacopeia traceability traceable to USP 1056504 Analysis Note These secondary standards offer multi-traceability to the USP, EP (PhEur) and BP primary standards, where they are available. General description Pharmaceutical secondary standards for application in quality control, provide pharma laboratories and manufacturers with a convenient and cost-effective alternative to the preparation of in-house working standards.FAQs of 1,4-Benzoquinone:
Q: What is the purity of 1,4-Benzoquinone?
A: The purity of 1,4-Benzoquinone is 98%.Q: What is the melting point of 1,4-Benzoquinone?
A: The melting point of 1,4-Benzoquinone is 115 C.Q: What is the molecular formula and molecular weight of 1,4-Benzoquinone?
A: The molecular formula of 1,4-Benzoquinone is C6H4O2, and its molecular weight is 108.095 g/mol.Q: What is the appearance of 1,4-Benzoquinone?
A: 1,4-Benzoquinone appears as a yellow solid.Q: What are the main usages of 1,4-Benzoquinone?
A: 1,4-Benzoquinone is primarily used as a hydrogen acceptor and oxidant in organic synthesis, a dehydrogenation reagent, and a dienophile in Diels-Alder reactions. It also reacts with acetic anhydride and sulfuric acid to produce the triacetate of hydroxyquinol.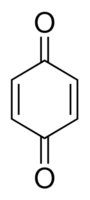
Tell us about your requirement

Price:
Quantity
Select Unit
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
Additional detail
Mobile number
Email
More Products in Analytical Grade Chemicals Category
Triadimenol A
Price 100 INR
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 , , Kilograms
Molecular Formula : C14H18ClN3O2
Molecular Weight : 295.76 Grams (g)
Appearance : Oil Based
Purity : 99%
-Decalactone
Price 100 INR
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Kilograms
Molecular Formula : C10H18O2
Molecular Weight : 170.25 Grams (g)
Appearance : Clear colorless to pale yellow liquid
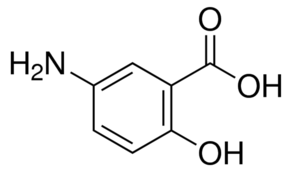
5-Aminosalicylic acid
Price 100 INR
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Kilograms
Molecular Formula : C7H8ClNO3
Molecular Weight : 189.595 Grams (g)
Purity : 99%
Bromomethane- 13C
Price 100 INR / Kilograms
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Kilograms
Molecular Formula : CH3Br
Appearance : Colorless gas with a chloroform
Purity : 99.8%

 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry

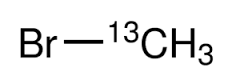


 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry Send SMS
Send SMS