Poly (tetrafluoroethylene)
MOQ : 1 Kilograms
Poly (tetrafluoroethylene) Specification
- Molecular Weight
- 100.02 Grams (g)
- Purity
- 99%
- Molecular Formula
- (C2F4)n
- Melting Point
- 326.8 C
- Usage
- PTFE is used as a non-stick coating for pans and other cookware. It is nonreactive, partly because of the strength of carbonfluorine bonds, and so it is often used in containers and pipework for reactive and corrosive chemicals.
Poly (tetrafluoroethylene) Trade Information
- Minimum Order Quantity
- 1 Kilograms
- Payment Terms
- Cash in Advance (CID), Cash Advance (CA)
- Supply Ability
- 500 Kilograms Per Month
- Delivery Time
- 2-8 Week
- Sample Available
- Yes
- Sample Policy
- Sample costs shipping and taxes has to be paid by the buyer
- Packaging Details
- Carton and Poly Bag.
- Main Export Market(s)
- Western Europe, Australia, Eastern Europe, Central America, Africa, Middle East, South America, Asia, North America
- Main Domestic Market
- All India
About Poly (tetrafluoroethylene)
Poly (tetrafluoroethylene), commonly known as PTFE, is a highly versatile material known for its exceptional non-stick properties and chemical inertness. With a molecular formula of (C2F4)n and a remarkable purity level of 99%, PTFE is ideal for applications that require resistance to reactive and corrosive chemicals. It is widely utilized as a non-stick coating for cookware, providing ease of use and maintenance. Additionally, PTFEs strong carbon-fluorine bonds ensure stability, making it suitable for containers and pipework used in industrial chemical handling. It exhibits a melting point of 326.8C and has a molecular weight of 100.02 grams (g), further affirming its robustness under high-temperature applications. As a reliable material, PTFE serves as a critical solution for demanding environments across various industries.
FAQs of Poly (tetrafluoroethylene):
Q: What are the primary uses of PTFE?
A: PTFE is used as a non-stick coating for cookware and in containers and pipework handling reactive and corrosive chemicals.Q: What is the purity level of PTFE?
A: PTFE has a purity level of 99%, making it highly reliable for industrial applications.Q: What is the melting point of PTFE?
A: The melting point of PTFE is 326.8C, allowing it to perform well under high temperatures.Q: Is PTFE chemically reactive?
A: No, PTFE is nonreactive due to the strength of its carbon-fluorine bonds.Q: What industries benefit from PTFE applications?
A: PTFE is widely utilized in cookware manufacturing, chemical processing, and industrial pipework systems.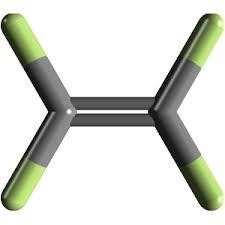
Tell us about your requirement

Price:
Quantity
Select Unit
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
Additional detail
Mobile number
Email
More Products in Analytical Grade Chemicals Category
Gasoline in Soil - AK - PT
Purity : Variable; depends on refining and additives
Molecular Weight : Variable typically around 100105 g/mol
Molecular Formula : CnH2n+2 (variable composition)
Appearance : Clear to slightly yellow liquid
Channel sediment (trace elements)
Purity : Depends on collection and extraction methods
Appearance : Powdery or grainy sediment typically brown or gray
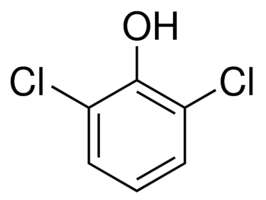
2,6-Dichlorophenol
Price 100 INR
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Kilograms
Purity : 99.3%
Molecular Weight : 163 Grams (g)
Molecular Formula : C6H4Cl2O
Appearance : White solid
Carbamates in Soil - PT
Price 100 INR
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Kilograms
Purity : 98%
Molecular Weight : 60.032 Grams (g)
Molecular Formula : CH2NO2

 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry


 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry Send SMS
Send SMS Call Me Free
Call Me Free