Trifluoroacetic acid
Trifluoroacetic acid Specification
- Melting Point
- -15.4 °C
- Molecular Formula
- C2HF3O2
- Solubility
- Miscible
- Usage
- Used to make other chemicals and as a solvent. At a low concentration, trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) is used as an ion pairing agent in liquid chromatography (HPLC) of organic compounds, particularly peptides and small proteins. TFA is a versatile solvent for NMR spectroscopy (for materials stable in acid).
- Molecular Weight
- 114.02 Grams (g)
Trifluoroacetic acid Trade Information
- Minimum Order Quantity
- 1 Kilograms
- Payment Terms
- Cash in Advance (CID), Cash Advance (CA)
- Supply Ability
- 500 Kilograms KG Per Month
- Delivery Time
- 2-8 Week
- Sample Available
- Yes
- Sample Policy
- Sample costs shipping and taxes has to be paid by the buyer
- Packaging Details
- Carton and Poly Bag.
- Main Export Market(s)
- Australia, Central America, Africa, Middle East, South America, Western Europe, Asia, Eastern Europe, North America
- Main Domestic Market
- All India
About Trifluoroacetic acid
FAQs of Trifluoroacetic acid:
Q: What is the primary usage of Trifluoroacetic acid?
A: Trifluoroacetic acid is primarily used to make other chemicals, as a solvent, and as an ion-pairing agent in HPLC for analyzing peptides and small proteins.Q: Can Trifluoroacetic acid be used in NMR spectroscopy?
A: Yes, TFA is a versatile solvent for NMR spectroscopy, provided the materials are stable in acidic conditions.Q: What is the molecular weight of Trifluoroacetic acid?
A: The molecular weight of Trifluoroacetic acid is 114.02 grams.Q: Is Trifluoroacetic acid fully miscible in solutions?
A: Yes, Trifluoroacetic acid is miscible, ensuring compatibility with various solvents.Q: At what temperature does Trifluoroacetic acid melt?
A: The melting point of Trifluoroacetic acid is -15.4 C.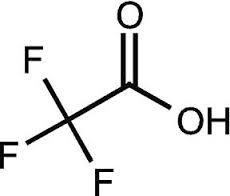

Price:
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
More Products in Analytical Grade Chemicals Category
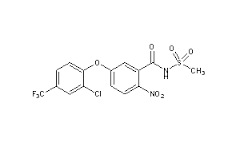
Fomesafen
Price 100 INR
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 , , Kilograms
Molecular Formula : C15H10ClF3N2O6S
Appearance : White to OffWhite Solid
Molecular Weight : 438.8 Grams (g)
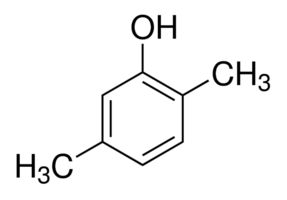
2,5-Dimethylphenol
Price 100 INR
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 , , Kiloampere
Purity : 98%
Molecular Formula : C8H10O
Appearance : colorless crystalline solid or brown chunky solid.
Molecular Weight : 122.16 Grams (g)
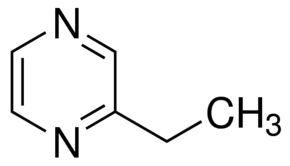
Ethylpyrazine
Price 100 INR
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Kilograms
Purity : 99%
Molecular Formula : C8H10N2O
Molecular Weight : 150.18 Grams (g)
1,4-Naphthoquinone solution
Price 100 INR
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 , , Kilograms
Purity : 93%
Molecular Formula : C10H6O2
Molecular Weight : 158.15 Grams (g)

 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry


 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry Send SMS
Send SMS